Publications
2022

E. C. Wood, Amy K. Glen, Lindsey G. Kvarfordt, Finn Womack, Liliana Acevedo, Timothy S. Yoon, Chunyu Ma, Veronica Flores, Meghamala Sinha, Yodsawalai Chodpathumwan, Arash Termehchy, Jared C. Roach, Luis Mendoza, Andrew S. Hoffman, Eric W. Deutsch, David Koslicki, Stephen A. Ramsey
BMC Bioinformatics · 29 Sep 2022 ·
Overview:
We develop RTX-KG2, a biomedical knowledge graph that uses an Extract-Transform-Load (ETL) approach to integrate 70 knowledge sources (including UMLS, SemMedDB, ChEMBL, DrugBank, SMPDB, and 65 additional knowledge sources) into a single knowledge graph and conforms to the Biolink standard metamodel.

Amy K. Glen, Chunyu Ma, Luis Mendoza, Finn Womack, E. C. Wood, Meghamala Sinha, Liliana Acevedo, Lindsey G. Kvarfordt, Ross C. Peene, Shaopeng Liu, Andrew S. Hoffman, Jared C. Roach, Eric W. Deutsch, Stephen A. Ramsey, David Koslicki
Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory · 16 Aug 2022 ·
Overview:
We introduce ARAX, a new reasoning system for translational biomedicine that provides a web browser user interface and an application programming interface. ARAX enables users to encode translational biomedical questions and to integrate knowledge across sources to answer the user9s query and facilitate exploration of results. For ARAX, we developed new approaches to query planning, knowledge-gathering, reasoning, and result ranking and dynamically integrate knowledge providers for answering biomedical questions.

Shaopeng Liu, David Koslicki
Bioinformatics · 24 Jun 2022 ·
Overview:
Utilizing truncation-based methods, we can obtain multi-resolution estimation of k-mer-based JI/CI in linear time for a range of k values.

Deepak R. Unni, Sierra A. T. Moxon, Michael Bada, Matthew Brush, Richard Bruskiewich, J. Harry Caufield, Paul A. Clemons, Vlado Dancik, Michel Dumontier, Karamarie Fecho, Gustavo Glusman, Jennifer J. Hadlock, Nomi L. Harris, Arpita Joshi, Tim Putman, Guangrong Qin, Stephen A. Ramsey, Kent A. Shefchek, Harold Solbrig, Karthik Soman, Anne E. Thessen, Melissa A. Haendel, Chris Bizon, Christopher J. Mungall, Liliana Acevedo, Stanley C. Ahalt, John Alden, Ahmed Alkanaq, Nada Amin, Ricardo Avila, Jim Balhoff, Sergio E. Baranzini, Andrew Baumgartner, William Baumgartner, Basazin Belhu, MacKenzie Brandes, Namdi Brandon, Noel Burtt, William Byrd, Jackson Callaghan, Marco Alvarado Cano, Steven Carrell, Remzi Celebi, James Champion, Zhehuan Chen, Mei‐Jan Chen, Lawrence Chung, Kevin Cohen, Tom Conlin, Dan Corkill, Maria Costanzo, Steven Cox, Andrew Crouse, Camerron Crowder, Mary E. Crumbley, Cheng Dai, Vlado Dančík, Ricardo De Miranda Azevedo, Eric Deutsch, Jennifer Dougherty, Marc P. Duby, Venkata Duvvuri, Stephen Edwards, Vincent Emonet, Nathaniel Fehrmann, Jason Flannick, Aleksandra M. Foksinska, Vicki Gardner, Edgar Gatica, Amy Glen, Prateek Goel, Joseph Gormley, Alon Greyber, Perry Haaland, Kristina Hanspers, Kaiwen He, Kaiwen He, Jeff Henrickson, Eugene W. Hinderer, Maureen Hoatlin, Andrew Hoffman, Sui Huang, Conrad Huang, Robert Hubal, Kenneth Huellas‐Bruskiewicz, Forest B. Huls, Lawrence Hunter, Greg Hyde, Tursynay Issabekova, Matthew Jarrell, Lindsay Jenkins, Adam Johs, Jimin Kang, Richa Kanwar, Yaphet Kebede, Keum Joo Kim, Alexandria Kluge, Michael Knowles, Ryan Koesterer, Daniel Korn, David Koslicki, Ashok Krishnamurthy, Lindsey Kvarfordt, Jay Lee, Margaret Leigh, Jason Lin, Zheng Liu, Shaopeng Liu, Chunyu Ma, Andrew Magis, Tarun Mamidi, Meisha Mandal, Michelle Mantilla, Jeffrey Massung, Denise Mauldin, Jason McClelland, Julie McMurry, Philip Mease, Luis Mendoza, Marian Mersmann, Abrar Mesbah, Matthew Might, Kenny Morton, Sandrine Muller, Arun Teja Muluka, John Osborne, Phil Owen, Michael Patton, David B. Peden, R. Carter Peene, Bria Persaud, Emily Pfaff, Alexander Pico, Elizabeth Pollard, Guthrie Price, Shruti Raj, Jason Reilly, Anders Riutta, Jared Roach, Ryan T. Roper, Greg Rosenblatt, Irit Rubin, Sienna Rucka, Nathaniel Rudavsky‐Brody, Rayn Sakaguchi, Eugene Santos, Kevin Schaper, Charles P. Schmitt, Shepherd Schurman, Erik Scott, Sarah Seitanakis, Priya Sharma, Ilya Shmulevich, Manil Shrestha, Shalki Shrivastava, Meghamala Sinha, Brett Smith, Noel Southall, Nicholas Southern, Lisa Stillwell, Michael “ Michi” Strasser, Andrew I. Su, Casey Ta, Anne E. Thessen, Jillian Tinglin, Lucas Tonstad, Thi Tran‐Nguyen, Alexander Tropsha, Gaurav Vaidya, Luke Veenhuis, Adam Viola, Marcin von Grotthuss, Max Wang, Patrick Wang, Paul B. Watkins, Rosina Weber, Qi Wei, Chunhua Weng, Jordan Whitlock, Mark D. Williams, Andrew Williams, Finn Womack, Erica Wood, Chunlei Wu, Jiwen Kevin Xin, Hao Xu, Colleen Xu, Chase Yakaboski, Yao Yao, Hong Yi, Arif Yilmaz, Marissa Zheng, Xinghua Zhou, Eric Zhou, Qian Zhu, Tom Zisk,
Clinical and Translational Science · 06 Jun 2022 ·
Overview:
Biolink Model is an open-source data model that can be used to formalize the relationships between data structures in translational science. It incorporates object-oriented classification and graph-oriented features. The core of the model is a set of hierarchical, interconnected classes (or categories) and relationships between them (or predicates) representing biomedical entities such as gene, disease, chemical, anatomic structure, and phenotype. The model provides class and edge attributes and associations that guide how entities should relate to one another. Here, we highlight the need for a standardized data model for KGs, describe Biolink Model, and compare it with other models.

Karamarie Fecho, Anne E. Thessen, Sergio E. Baranzini, Chris Bizon, Jennifer J. Hadlock, Sui Huang, Ryan T. Roper, Noel Southall, Casey Ta, Paul B. Watkins, Mark D. Williams, Hao Xu, William Byrd, Vlado Dančík, Marc P. Duby, Michel Dumontier, Gustavo Glusman, Nomi L. Harris, Eugene W. Hinderer, Greg Hyde, Adam Johs, Andrew I. Su, Guangrong Qin, Qian Zhu, Liliana Acevedo, Stanley C. Ahalt, John Alden, Ahmed Alkanaq, Nada Amin, Ricardo Avila, Michael Bada, Jim Balhoff, Andrew Baumgartner, William Baumgartner, Basazin Belhu, Mac Kenzie Brandes, Namdi Brandon, Matthew Brush, Richard Bruskiewich, Noel Burtt, Jackson Callaghan, Marco Alvarado Cano, Steven Carrell, J. Harry Caufield, Remzi Celebi, James Champion, Zhehuan Chen, Mei‐Jan Chen, Lawrence Chung, Paul A. Clemons, Kevin Cohen, Tom Conlin, Dan Corkill, Maria Costanzo, Steven Cox, Andrew Crouse, Camerron Crowder, Mary E. Crumbley, Cheng Dai, Ricardo De Miranda Azevedo, Eric Deutsch, Jennifer Dougherty, Venkata Duvvuri, Stephen Edwards, Vincent Emonet, Nathaniel Fehrmann, Jason Flannick, Aleksandra M. Foksinska, Vicki Gardner, Edgar Gatica, Amy Glen, Prateek Goel, Joseph Gormley, Alon Greyber, Perry Haaland, Melissa A. Haendel, Kristina Hanspers, Kaiwen He, Jeff Henrickson, Maureen Hoatlin, Andrew Hoffman, Conrad Huang, Robert Hubal, Kenneth Huellas‐Bruskiewicz, Forest B. Huls, Lawrence Hunter, Tursynay Issabekova, Matthew Jarrell, Lindsay Jenkins, Arpita Joshi, Jimin Kang, Richa Kanwar, Yaphet Kebede, Keum Joo Kim, Alexandria Kluge, Michael Knowles, Ryan Koesterer, Daniel Korn, David Koslicki, Ashok Krishnamurthy, Lindsey Kvarfordt, Jay Lee, Margaret Leigh, Jason Lin, Zheng Liu, Shaopeng Liu, Chunyu Ma, Andrew Magis, Tarun Mamidi, Meisha Mandal, Michelle Mantilla, Jeffrey Massung, Denise Mauldin, Jason McClelland, Julie McMurry, Philip Mease, Luis Mendoza, Marian Mersmann, Abrar Mesbah, Matthew Might, Kenny Morton, Sierra A. T. Moxon, Sandrine Muller, Arun Teja Muluka, Christopher J. Mungall, John Osborne, Phil Owen, Michael Patton, David B. Peden, R. Carter Peene, Bria Persaud, Emily Pfaff, Alexander Pico, Elizabeth Pollard, Guthrie Price, Tim Putman, Shruti Raj, Stephen A. Ramsey, Jason Reilly, Anders Riutta, Jared Roach, Greg Rosenblatt, Irit Rubin, Sienna Rucka, Nathaniel Rudavsky‐Brody, Rayn Sakaguchi, Eugene Santos, Kevin Schaper, Charles P. Schmitt, Shepherd Schurman, Erik Scott, Sarah Seitanakis, Priya Sharma, Kent A. Shefchek, Ilya Shmulevich, Manil Shrestha, Shalki Shrivastava, Meghamala Sinha, Brett Smith, Harold Solbrig, Karthik Soman, Nicholas Southern, Lisa Stillwell, Michael “ Michi” Strasser, Anne E. Thessen, Jillian Tinglin, Lucas Tonstad, Thi Tran‐Nguyen, Alexander Tropsha, Deepak R. Unni, Gaurav Vaidya, Luke Veenhuis, Adam Viola, Marcin von Grotthuss, Max Wang, Patrick Wang, Rosina Weber, Qi Wei, Chunhua Weng, Jordan Whitlock, Andrew Williams, Finn Womack, Erica Wood, Chunlei Wu, Jiwen Kevin Xin, Colleen Xu, Chase Yakaboski, Yao Yao, Hong Yi, Arif Yilmaz, Marissa Zheng, Xinghua Zhou, Eric Zhou, Tom Zisk,
Clinical and Translational Science · 06 Jun 2022 ·
Overview:
The Biomedical Data Translator Consortium has developed and tested a pilot knowledge graph-based “Translator” system capable of integrating existing biomedical data sets and “translating” those data into insights intended to augment human reasoning and accelerate translational science.

Varuni Sarwal, Jaqueline Brito, Serghei Mangul, David Koslicki
Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory · 29 Apr 2022 ·
Overview:
Here we report the development of TAMPA (Taxonomic metagenome profiling evaluation) , a robust and easy-to-use method that allows scientists to easily interpret and interact with taxonomic profiles produced by the many different taxonomic profiler methods beyond the standard metrics used by the scientific community. We demonstrate the unique ability of TAMPA to provide important biological insights into the taxonomic differences between samples otherwise missed by commonly utilized metrics. Additionally, we show that TAMPA can help visualize the output of taxonomic profilers, enabling biologists to effectively choose the most appropriate profiling method to use on their metagenomics data.

Fernando Meyer, Adrian Fritz, Zhi-Luo Deng, David Koslicki, Till Robin Lesker, Alexey Gurevich, Gary Robertson, Mohammed Alser, Dmitry Antipov, Francesco Beghini, Denis Bertrand, Jaqueline J. Brito, C. Titus Brown, Jan Buchmann, Aydin Buluç, Bo Chen, Rayan Chikhi, Philip T. L. C. Clausen, Alexandru Cristian, Piotr Wojciech Dabrowski, Aaron E. Darling, Rob Egan, Eleazar Eskin, Evangelos Georganas, Eugene Goltsman, Melissa A. Gray, Lars Hestbjerg Hansen, Steven Hofmeyr, Pingqin Huang, Luiz Irber, Huijue Jia, Tue Sparholt Jørgensen, Silas D. Kieser, Terje Klemetsen, Axel Kola, Mikhail Kolmogorov, Anton Korobeynikov, Jason Kwan, Nathan LaPierre, Claire Lemaitre, Chenhao Li, Antoine Limasset, Fabio Malcher-Miranda, Serghei Mangul, Vanessa R. Marcelino, Camille Marchet, Pierre Marijon, Dmitry Meleshko, Daniel R. Mende, Alessio Milanese, Niranjan Nagarajan, Jakob Nissen, Sergey Nurk, Leonid Oliker, Lucas Paoli, Pierre Peterlongo, Vitor C. Piro, Jacob S. Porter, Simon Rasmussen, Evan R. Rees, Knut Reinert, Bernhard Renard, Espen Mikal Robertsen, Gail L. Rosen, Hans-Joachim Ruscheweyh, Varuni Sarwal, Nicola Segata, Enrico Seiler, Lizhen Shi, Fengzhu Sun, Shinichi Sunagawa, Søren Johannes Sørensen, Ashleigh Thomas, Chengxuan Tong, Mirko Trajkovski, Julien Tremblay, Gherman Uritskiy, Riccardo Vicedomini, Zhengyang Wang, Ziye Wang, Zhong Wang, Andrew Warren, Nils Peder Willassen, Katherine Yelick, Ronghui You, Georg Zeller, Zhengqiao Zhao, Shanfeng Zhu, Jie Zhu, Ruben Garrido-Oter, Petra Gastmeier, Stephane Hacquard, Susanne Häußler, Ariane Khaledi, Friederike Maechler, Fantin Mesny, Simona Radutoiu, Paul Schulze-Lefert, Nathiana Smit, Till Strowig, Andreas Bremges, Alexander Sczyrba, Alice Carolyn McHardy
Nature Methods · 01 Apr 2022 ·
Overview:
We analyze and present the results of the second round of the CAMI competition. Over 5,000 results were submitted by 76 different metagenomic tools covering the tasks of assembly, binning, and profiling.

David Koslicki, Dana Gibbon, Mark Novak
F1000Research · 11 Feb 2022 ·
Overview:
Here, we introduce PressPurt , a computational package for identifying the interactions whose strengths must be estimated most accurately in order to produce robust predictions of a network’s response to press perturbations. The package provides methods for calculating and visualizing these edge-specific sensitivities (tolerances) when uncertainty is associated to one or more edges according to a variety of different error distributions. The software requires the network to be represented as a numerical (quantitative or qualitative) Jacobian matrix evaluated at stable equilibrium.

Antonio Blanca, Robert S. Harris, David Koslicki, Paul Medvedev
Journal of Computational Biology · 01 Feb 2022 ·
Overview:
We derive the expectation and variance of the number of mutated k-mers and of the number of islands (a maximal interval of mutated k-mers) and oceans (a maximal interval of nonmutated k-mers). We then derive hypothesis tests and confidence intervals (CIs) for r given an observed number of mutated k-mers, or, alternatively, given the Jaccard similarity (with or without MinHash).

Mahdi Belbasi, Antonio Blanca, Robert S. Harris, David Koslicki, Paul Medvedev
Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory · 17 Jan 2022 ·
Overview:
We show that the minimizer Jaccard estimator is biased and inconsistent, which means that the expected difference (i.e., the bias) between the estimator and the true value is not zero, even in the limit as the lengths of the sequences grow. We derive an analytical formula for the bias as a function of how the shared k-mers are laid out along the sequences. We show both theoretically and empirically that there are families of sequences where the bias can be substantial (e.g. the true Jaccard can be more than double the estimate). Finally, we demonstrate that this bias affects the accuracy of the widely used mashmap read mapping tool.

Mahmudur Rahman Hera, N. Tessa Pierce-Ward, David Koslicki
Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory · 12 Jan 2022 ·
Overview:
In this paper, we theoretically analyzed FracMinHash, proved a bias in the estimator, and finally showed how to debias the estimator. We then showed how this FracMinHash estimator can be used to estimate the evolutionary distance of two genomes. Our results show that mutation rates determined by our analyses are more accurate across a wider range of evolutionary distances compared to classical MinHash techniques.

Luiz Irber, Phillip T. Brooks, Taylor Reiter, N. Tessa Pierce-Ward, Mahmudur Rahman Hera, David Koslicki, C. Titus Brown
Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory · 12 Jan 2022 ·
Overview:
Implementation of FracMinHash sketching technique into sourmash software package, and analysis of FracMinHash in shotgun metagenome compositional analysis after modeling the problem as minimum metagenome cover

Wei Wei, David Koslicki
Schloss Dagstuhl - Leibniz-Zentrum für Informatik · 01 Jan 2022 ·
Overview:
In this study, we demonstrate a method to overcome this intrinsic difference and compute the UniFrac metric on WGS data by assigning branch lengths to the taxonomic tree obtained from input taxonomic profiles. We conduct a series of experiments to demonstrate that this WGSUniFrac method is comparably robust to traditional 16S UniFrac and is not highly sensitive to branch lengths assignments, be they data-derived or model-prescribed.
2021

Mohammed Alser, Jeremy Rotman, Dhrithi Deshpande, Kodi Taraszka, Huwenbo Shi, Pelin Icer Baykal, Harry Taegyun Yang, Victor Xue, Sergey Knyazev, Benjamin D. Singer, Brunilda Balliu, David Koslicki, Pavel Skums, Alex Zelikovsky, Can Alkan, Onur Mutlu, Serghei Mangul
Genome Biology · 26 Aug 2021 ·
Overview:
We provide a systematic survey of 107 long and short read alignment tools and analyze how alignment algorithms have co-evolved with sequencing technology advancements, as well as how these algorithmic changes affect tool performance.
Karamarie Fecho, James Balhoff, Chris Bizon, William E. Byrd, Sui Hang, David Koslicki, Stefano E. Rensi, Patrick L. Schmitt, Mathias J. Wawer, Mark Williams, Stanley C. Ahalt
Clinical and Translational Science · 09 Apr 2021 ·
Overview:
Reasoning system based on knowledge graphs.

Fernando Meyer, Till-Robin Lesker, David Koslicki, Adrian Fritz, Alexey Gurevich, Aaron E. Darling, Alexander Sczyrba, Andreas Bremges, Alice C. McHardy
Nature Protocols · 01 Mar 2021 ·
Overview:
Tutorial for using CAMI toolkits to access metagenomic software.
2020

Nathan LaPierre, Mohammed Alser, Eleazar Eskin, David Koslicki, Serghei Mangul
Genome Biology · 10 Sep 2020 ·
Overview:
Utilizing a pre-filter strategy, Metalign performs efficient and accurate alignment-based metagenomic profiling through the estimation of contaiment indices of pre-built reference databases.

Caitlin Loeffler, Keylie M. Gibson, Lana Martin, Liz Chang, Jeremy Rotman, Ian V. Toma, Christopher E. Mason, Eleazar Eskin, Joseph P. Zackular, Keith A. Crandall, David Koslicki, Serghei Mangul
arXiv · 11 Aug 2020 ·
Overview:
We present an overview of metagenomics methods with a discussion of computational challenges and limitations.

Caitlin Loeffler, Aaron Karlsberg, Lana S. Martin, Eleazar Eskin, David Koslicki, Serghei Mangul
BMC Biology · 07 Apr 2020 ·
Overview:
We analyze and discuss guidelines for the development of a master reference database for disparate reference databases.

Simon Foucart, David Koslicki
arXiv · 24 Jan 2020 ·
Overview:
We leverage a recently developed notion of biological diversity that simultaneously accounts for organism similarities and retains the optimization strategy underlying compressive-sensing-based approaches.
2019

Finn Womack, Jason McClelland, David Koslicki
Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory · 11 Sep 2019 ·
Overview:
We leverage a graph-based approach to integrate biological knowledge and then employ a graph node embedding scheme to make novel predictions about current drugs.

David Koslicki, Hooman Zabeti
Applied Mathematics and Computation · 01 Aug 2019 ·
Overview:
This work improves upon the so called “min hash” technique (a “probabilistic data analysis” method) to develop a very fast and efficient way to estimate the similarity of two sets of objects (in terms of how much they overlap). The approach we present is orders of magnitude faster (and uses orders of magnitude less space) when two data sets under consideration are of very different size. The kinds of sets we consider are sets of sub-strings (called k-mers) of DNA sequences from communities of microorganisms.

Nathan LaPierre, Serghei Mangul, Mohammed Alser, Igor Mandric, Nicholas C. Wu, David Koslicki, Eleazar Eskin
BMC Genomics · 01 Jun 2019 ·
Overview:
We show that read mapping, along with a probabilistic assignment of multi-mapped reads, outperforms other computational approaches to identify the presence and relative amount of viral and fungal organisms in a metagenomic sample of microorganismal DNA.
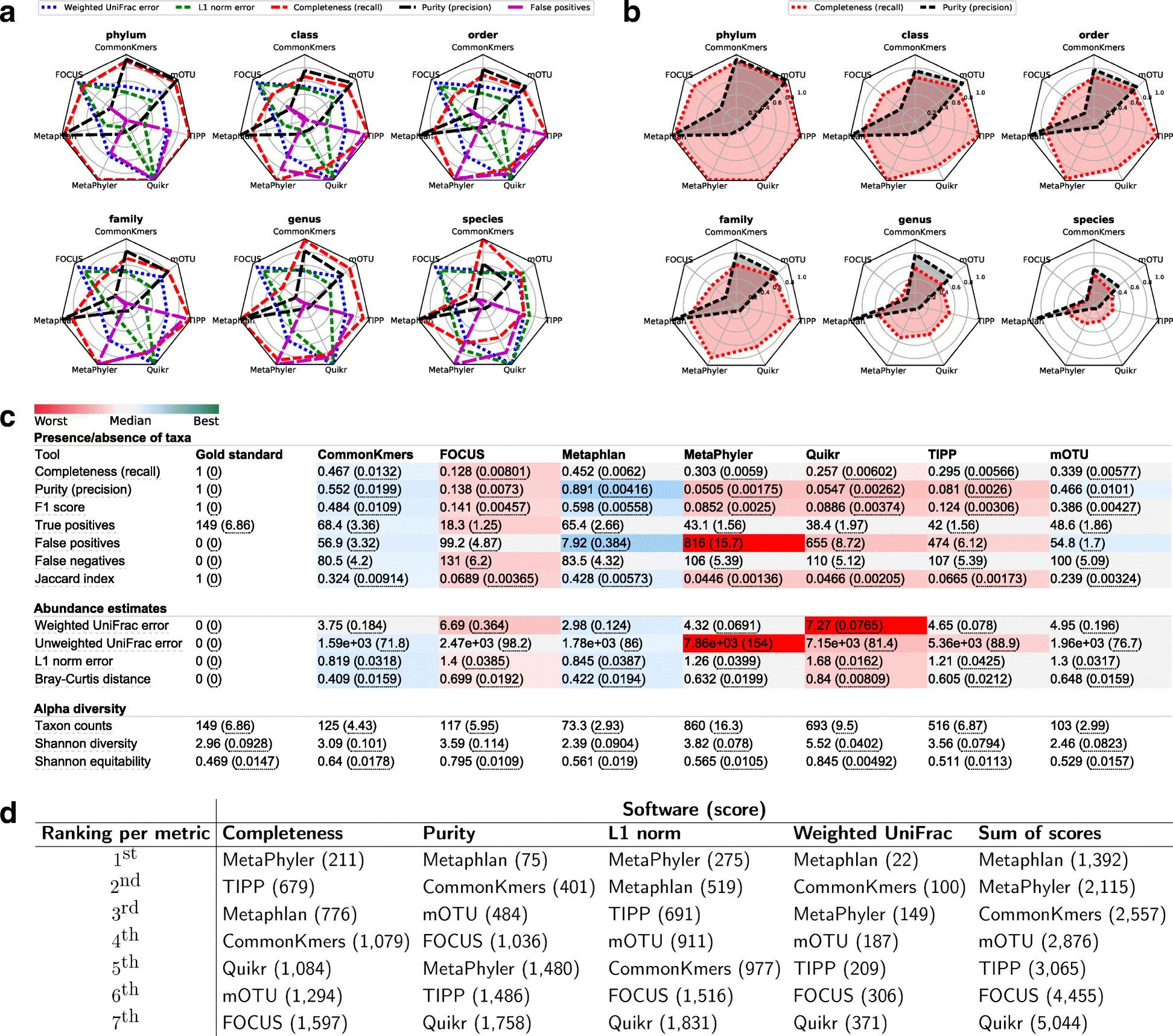
Fernando Meyer, Andreas Bremges, Peter Belmann, Stefan Janssen, Alice C. McHardy, David Koslicki
Genome Biology · 04 Mar 2019 ·
Overview:
We introduce a framework to compare tools utilized to determine what microbes are present in a sample, and at what relative abundance. This will help computational biologists design better tools to analyze communities of microorganisms (which affect nearly everything in existence!).
2018

Clinical and Translational Science · 09 Nov 2018 ·
Overview:
A description of the NIH NCATS culture that emerged during the Translator project.

Clinical and Translational Science · 09 Nov 2018 ·
Overview:
The vision and high-level overview of the NIH National Center for Advancing Translational Science (NCATS) project entitled “Translator” (through which we have been funded). The goal of the project is essentially to build a biomedical “Siri”: an automated platform for answering biomedical research questions that leverages repositories of publicly available information.

Loes M. Olde Loohuis, Serghei Mangul, Anil P. S. Ori, Guillaume Jospin, David Koslicki, Harry Taegyun Yang, Timothy Wu, Marco P. Boks, Catherine Lomen-Hoerth, Martina Wiedau-Pazos, Rita M. Cantor, Willem M. de Vos, René S. Kahn, Eleazar Eskin, Roel A. Ophoff
Translational Psychiatry · 10 May 2018 ·
Overview:
Along with collaborators at UCLA, we were able to detect a small, but significant amount of microbes in blood This is surprising since it’s typically assumed that the immune system typically removes any microbial presence from human blood. I used a reference-free microbial community algorithm, called EMDeBruijn, to help corroborate the patterns we saw which included an increase in microbial diversity in schizophrenia patients. EMDeBruijn is a metric based on the Wasserstein metric (aka the Earth Mover’s Distance) and a de Bruijn graph induced by the k-mers in a metagenomic DNA sample.

Jason McClelland, David Koslicki
Journal of Mathematical Biology · 25 Apr 2018 ·
Overview:
Rapidly answers “why are these data sets different” by leveraging hierarchical/relatedness information. In short, we develop an algorithm to quickly compute the Unifrac distance by leveraging the earth mover’s distance, prove its correctness, and derive time and space complexity characterizations.
2017

Mitra Ansariola, Molly Megraw, David Koslicki
Bioinformatics · 11 Dec 2017 ·
Overview:
A gene regulatory network is basically a representation of how genes interact with each other. In this work, we develop the only (to date) method to assess the accuracy of so called “motif discovery algorithms” that seek to find important sub-networks of a given gene regulatory network. We develop a provably correct mathematical approach (based on a variety of metrics that say how close two matrices are to each other) and use this to assess the performance of a variety of motif discovery algorithms.

Alexander Sczyrba, Peter Hofmann, Peter Belmann, David Koslicki, Stefan Janssen, Johannes Dröge, Ivan Gregor, Stephan Majda, Jessika Fiedler, Eik Dahms, Andreas Bremges, Adrian Fritz, Ruben Garrido-Oter, Tue Sparholt Jørgensen, Nicole Shapiro, Philip D Blood, Alexey Gurevich, Yang Bai, Dmitrij Turaev, Matthew Z DeMaere, Rayan Chikhi, Niranjan Nagarajan, Christopher Quince, Fernando Meyer, Monika Balvočiūtė, Lars Hestbjerg Hansen, Søren J Sørensen, Burton K H Chia, Bertrand Denis, Jeff L Froula, Zhong Wang, Robert Egan, Dongwan Don Kang, Jeffrey J Cook, Charles Deltel, Michael Beckstette, Claire Lemaitre, Pierre Peterlongo, Guillaume Rizk, Dominique Lavenier, Yu-Wei Wu, Steven W Singer, Chirag Jain, Marc Strous, Heiner Klingenberg, Peter Meinicke, Michael D Barton, Thomas Lingner, Hsin-Hung Lin, Yu-Chieh Liao, Genivaldo Gueiros Z Silva, Daniel A Cuevas, Robert A Edwards, Surya Saha, Vitor C Piro, Bernhard Y Renard, Mihai Pop, Hans-Peter Klenk, Markus Göker, Nikos C Kyrpides, Tanja Woyke, Julia A Vorholt, Paul Schulze-Lefert, Edward M Rubin, Aaron E Darling, Thomas Rattei, Alice C McHardy
Nature Methods · 02 Oct 2017 ·
Overview:
In a very reproducible fashion, we assess a wide variety of computational techniques in metagenomics, including assembly (putting together pieces of genomes, called contigs, from short reads), binning (figuring out where the contigs came from), and taxonomic profiling (determining which organisms are present in a sample and at what relative amount).

David Koslicki, Mark Novak
Journal of Mathematical Biology · 22 Jul 2017 ·
Overview:
In a network of interacting quantities (such as a food web), we examine how qualitative and quantitative predictions change when a quantity (such as the abundance of an organism or a set of organisms) is increased. This is quantified in terms of which model parameters cause the largest change in predictions.
2016

David Koslicki, Manfred Denker
Rocky Mountain Journal of Mathematics · 01 Dec 2016 ·
Overview:
After introducing the notion of a random substitution Markov chain, we relate it to other notions of a “random substitution” and give a complete description of the Martin boundary for a few interesting examples.

Serghei Mangul, David Koslicki
Proceedings of the 7th ACM International Conference on Bioinformatics, Computational Biology, and Health Informatics · 02 Oct 2016 ·
Overview:
We present the idea of using the “earth mover’s distance” (aka the first Wasserstein metric) to measure the distance between samples of DNA. This reduces to finding the most efficient way to transform one kind of graph (known as de Bruijn graphs) into another.

David Koslicki, Daniel Falush
mSystems · 28 Jun 2016 ·
Overview:
We present a computational technique that answers the question “Which organisms are present in a given sample of of DNA from a microbial community, and at what relative amount” while simultaneously predicting the relatedness of novel (never-before seen organisms) in relation to known organisms. This relies on a mathematical technique referred to as sparsity-promoting optimization and relies on a technique similar to the Jaccard index.
2015

David Koslicki, Saikat Chatterjee, Damon Shahrivar, Alan W. Walker, Suzanna C. Francis, Louise J. Fraser, Mikko Vehkaperä, Yueheng Lan, Jukka Corander
PLOS ONE · 23 Oct 2015 ·
Overview:
We develop a pre-processing step that significantly improves k-mer based metagenomic profiling techniques.
2014

S. Chatterjee, D. Koslicki, S. Dong, N. Innocenti, L. Cheng, Y. Lan, M. Vehkapera, M. Skoglund, L. K. Rasmussen, E. Aurell, J. Corander
Bioinformatics · 07 May 2014 ·
Overview:
In this paper, we improve both the accuracy and speed of the Quikr approach to classifying a given set of metagenomic DNA sequences (16S rRNA). This is accomplished by increasing the number of “feature vectors” we use for each training genome, and by modifying the Lawson-Hanson algorithm for non-negative least squares.

Simon Foucart, David Koslicki
IEEE Signal Processing Letters · 01 Apr 2014 ·
Overview:
We prove that nonnegative least squares (typically prone to over-fitting) can be slightly modified to return sparse results.

David Koslicki, Simon Foucart, Gail Rosen
PLoS ONE · 13 Mar 2014 ·
Overview:
Extending the results of Quikr to whole genome shotgun metagenomic samples, we develop a method to automatically select a parameter that balances sparsity (how succinct the result is) with accuracy.

David Koslicki, Daniel J. Thompson
Journal of Mathematical Biology · 22 Jan 2014 ·
Overview:
We demonstrate that a concept of “weighted information content” (known as topological pressure, from the ergodic theory literature) can be used to facilitate the analysis of genomic data (in particular, find areas of a genome that have many genes in them). This is a conceptual extension to topological entropy approach presented earlier.

Andreas Holzinger, Matthias Hörtenhuber, Christopher Mayer, Martin Bachler, Siegfried Wassertheurer, Armando J. Pinho, David Koslicki
Interactive Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining in Biomedical Informatics · 01 Jan 2014 ·
Overview:
We review a variety of entropy/randomness-based techniques that are useful in a variety of data mining applications.
2013

David Koslicki, Simon Foucart, Gail Rosen
Bioinformatics · 20 Jun 2013 ·
Overview:
We introduce an extremely fast, light-weight, “big data” algorithm to quickly answer the question of “which bacteria are present?” in a given sample of DNA. The method is based on the theory of compressed sensing and aims to find the simplest explanation for the data in terms of known information.
2011

David Koslicki
Bioinformatics · 10 Feb 2011 ·
Overview:
I define a new notion of “randomness” (called topological pressure) suitable for use on sequences of symbols (words) of finite length. I show that this can be used to distinguish between biologically interesting sequences in the human genome.
More
The citations on this page were generated automatically from just identifiers using the Manubot cite utility developed in the Greene Lab!
